86. Electrochemical valorization of H2S in natural gas to sulfate under mild conditions
Chunyu Zhang, An-Zhen Li, Bo-Jun Yuan, Xiang Liu, Yuanbo Liu, Kejian Kong, Qiujin Shi, Yixuan Zhang, Yiqi Luo, Shengnan Li, Hua Zhou* & Haohong Duan*
Nat. commun. 2025,16, 7175
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62445-y
Abstract
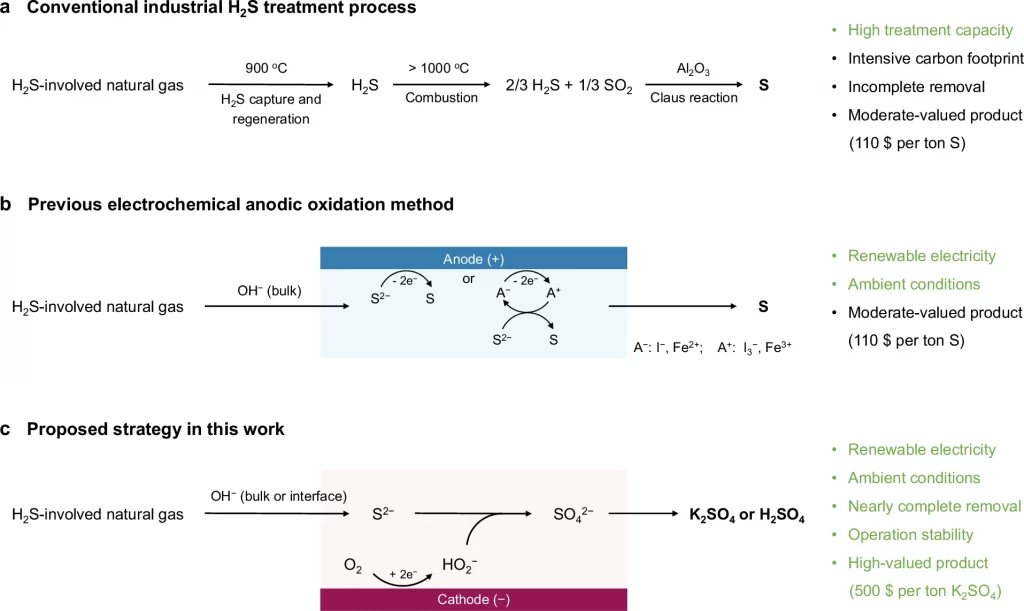
H2S capture and valorization from polluted natural gas offer environmental and resource recovery benefits, but current approaches produce moderate-value sulfur with intensive carbon footprint. Herein, we develop an electrochemical deep oxidation method that converts H2S from polluted natural gas into value-added K2SO4 using in-situ cathodically generated H2O2. We first validate this concept using commercial H2O2 and then in-situ generated H2O2 in H-cell, revealing the importance of high H2O2 concentration for deep H2S oxidation, especially sluggish S2O32−-to-SO32− conversion. We then showcase its application potential in 4-cm2 and then 100-cm2 flow reactor with high interfacial H2O2 concentration and large current, with the latter achieving H2S removal (100,000 ppm to <15 ppm), >70% K2SO4 selectivity, and 100-h stable operation. Life-cycle assessment and techno-economic analysis confirm the strategy’s sustainability advantages and economic viability. We finally extend this method to produce a 1.4 wt% H2SO4 solution by modifying the flow reactor with a solid-electrolyte type.