87. Selective electrooxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural at pilot scale by engineering a solid polymer electrolyte reactor
Yue Ren, Wei Kong, Yang Li, Wang Zhan, Chunyu Zhang, Yuhang Miao, Bingxin Yao, Shengnan Li, Zhenhua Li, Xiang Liu,Sheng Zhan, Hua Zhou*, Mingfei Shao* & Haohong Duan*
Nat. Catal. 2025, 8, 771–783
DOI: 10.1038/s41929-025-01374-x
Abstract
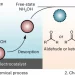
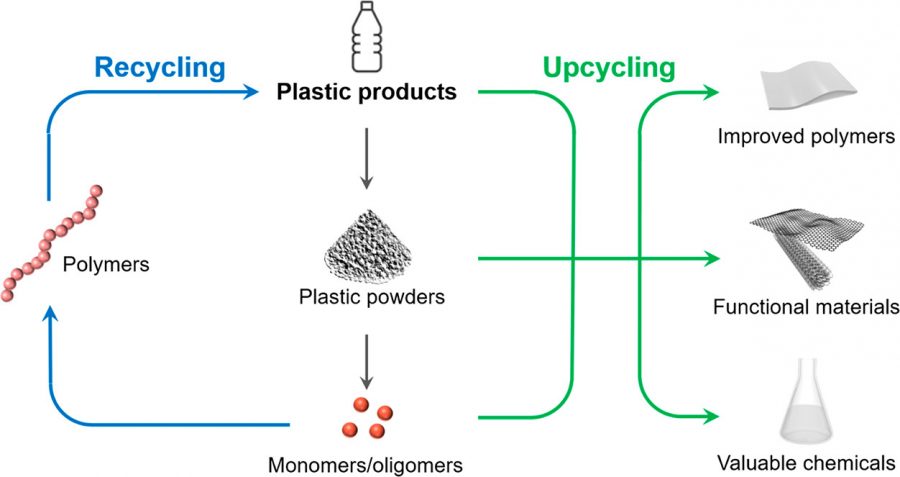
Aqueous electrolysis offers a potential sustainable route for converting biomass derivatives to plastic monomers, such as 5-hydroxymethylfurfural oxidation to 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA). However, selective electrosynthesis of high-concentration FDCA at kilowatt scale and ampere-level current density remains an unmet challenge, hindering commercialization. Here we show an engineered solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) reactor to steer Faradaic and non-Faradaic side reactions, achieving FDCA production at an industrially relevant current density (1.5 A cm−2) while maintaining high selectivity (97.0%), Faradaic efficiency (88.2%) and concentration (~1.24 M). The stability of the SPE reactor was demonstrated in continuous operation at 0.5 A cm−2 over 140 h. Moreover, a 4.3-kW electrochemical platform was constructed with a scale-out strategy, reaching a pilot-scale FDCA production rate (33 kg per day). This work shows the capability of reactor engineering to enable selective and large-scale production of sustainable chemicals via electrochemical processes.